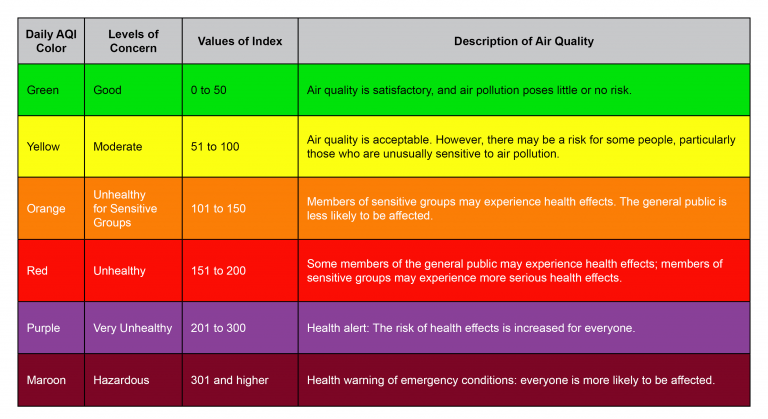
The Air Quality Index (AQI) reports daily air quality information. It is calculated for five of the six major criteria air pollutants regulated by the federal Clean Air Act: ground-level ozone, particle pollution, carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide. EPA established national ambient air quality standards for each pollutant to protect public health.
The AQI is a national index and the value and colors are the same across the United States. The higher the AQI value, the greater the level of air pollution and health risk.
An AQI of 100 is the level set by EPA for each pollutant to protect public health. An AQI above 100 is considered unhealthy for certain sensitive groups. As AQI increases, air quality becomes unhealthy for the general public. For more information on AQI health precautions, visit our Air Quality Forecasts page and EPA’s AirNow pages.